Alzheimer's Disease Risk & Cognitive Decline Panel
Early detection of Alzheimer's disease is possible years before symptoms begin. Our comprehensive panel combines genetic, molecular, and biomarker analysis with reversible cause screening — empowering you and your clinician to take proactive steps against cognitive decline.
Alzheimer’s Disease Risk & Cognitive Decline Panel
Genetic Risk Marker
- APOE Genotype
- ε4 allele increases risk of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease.
- Useful for risk stratification and counseling, but not deterministic.
ATN Profile (Core Alzheimer’s Biomarkers)
- A = Amyloid
- Aβ42, Aβ40, and Aβ42/40 ratio (plasma or CSF)
- Low ratio suggests amyloid accumulation.
- T = Tau
- p-tau181 (or p-tau217, p-tau231 if available)
- Elevated levels are highly specific for Alzheimer’s pathology.
- N = Neurodegeneration
- NfL (Neurofilament Light Chain)
- MRI volumetrics (hippocampal atrophy) or FDG-PET optional.
Reversible / Secondary Causes of Cognitive Impairment
- Thyroid
- TSH (hypothyroidism can mimic dementia).
- Infectious
- RPR (syphilis serology).
- Lyme antibody panel (Borrelia infection can cause cognitive issues).
- ANA (antinuclear antibody) — screens for autoimmune/inflammatory causes.
- Nutritional / Metabolic
- B12
- Methylmalonic Acid (MMA) — more sensitive indicator of functional B12 deficiency.
- ESR (Sedimentation Rate) — marker of systemic inflammation.
Clinical Use
- Baseline risk stratification: APOE + ATN profile.
- Rule out treatable causes: thyroid, B12, infections, autoimmune.
- Guide intervention: tailor prevention (lifestyle, vascular risk control, supplements, clinical trial eligibility).
Detect Early Changes with the ATN Framework
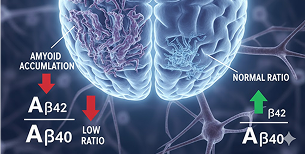
A (Amyloid)
Aβ42, Aβ40, Aβ42/40 ratio
Low ratio indicates amyloid accumulation
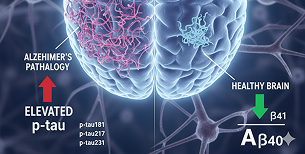
T (Tau)
p-tau181 (or p-tau217/p-tau231)
Elevated levels signal Alzheimer's-specific pathology.
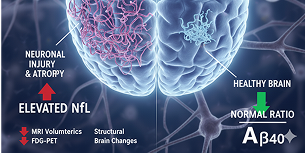
N (Neurodegeneration)
Neurofilament Light Chain (NfL), MRI volumetrics, FDG-PET
Indicates neuronal injury and structural loss.
Rule Out Treatable Causes of Cognitive Decline
Thyroid
-
 TSH – screens
for hypothyroidism
TSH – screens
for hypothyroidism
Infectious
-
 RPR –
syphilis
RPR –
syphilis -
 Lyme antibody
panel
Lyme antibody
panel -
 ANA –
autoimmune causes
ANA –
autoimmune causes
Nutritional / Metabolic
-
 Vitamin
B12
Vitamin
B12 -
 MMA –
functional B12 deficiency
MMA –
functional B12 deficiency -
 ESR –
inflammation marker
ESR –
inflammation marker
Clinical Utility

How This Panel Helps You
-
 Baseline risk assessment (APOE +
ATN)
Baseline risk assessment (APOE +
ATN) -
 Identify treatable causes
Identify treatable causes -
 Guide personalized prevention
strategies
Guide personalized prevention
strategies -
 Inform clinical trial eligibility
Inform clinical trial eligibility
